When it comes to workplace safety, fall protection is one of the most critical aspects to address. Falls are a leading cause of workplace injuries and fatalities, which is why the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established clear standards for fall protection to safeguard workers in a variety of industries.
In this blog post, we’ll dive into the OSHA fall protection standards, explore the requirements, and explain how businesses can comply to ensure a safe work environment.
_________________
Overview of OSHA Fall Protection Standards
OSHA's fall protection standards are designed to prevent accidents and injuries from falls in the workplace. These standards apply to industries like construction, general industry, and shipyard employment. The specific requirements depend on the nature of the work and the height at which it is performed.
Here are the key OSHA standards for fall protection:
-
Construction Industry - 29 CFR 1926 Subpart M
In construction, fall protection is required at heights of 6 feet or more. Employers must provide appropriate safety systems such as guardrails, safety nets, or personal fall arrest systems (PFAS).
-
General Industry - 29 CFR 1910 Subpart D
For general industry, fall protection is required at heights of 4 feet or more. Guardrails, covers, or safety harnesses must be used to protect workers from falling.
-
Shipyard Employment - 29 CFR 1915 Subpart I
Fall protection is mandated at heights of 5 feet or more in shipyard operations. Employers must also account for specific hazards, such as working near open hatches or along edges.
-
Special Considerations
- In scaffolding work, the threshold for fall protection is typically 10 feet or more (per 29 CFR 1926.451).
-
Ladder safety systems may be required depending on the type of ladder and height of use.
- In situations with potential falling object hazards, OSHA requires measures like toe boards, screens, or debris nets.
_________________
Key Elements of OSHA-Compliant Fall Protection
1. Hazard Assessment
Employers must evaluate the workplace to identify potential fall hazards. This includes assessing walking/working surfaces, structural integrity, and environmental risks.
2. Fall Protection Systems
OSHA allows for a variety of fall protection systems, including:
-
Guardrails: A physical barrier to prevent falls.
-
Safety Nets: Installed below work areas to catch falling workers.
-
Personal Fall Arrest Systems (PFAS): Includes a harness, lanyard, and anchor point to stop a fall in progress.
-
Positioning Systems: Keeps workers securely positioned while working at height.
3. Training
Under OSHA's regulations, employers must train workers on recognizing fall hazards and using fall protection systems properly. Training should include inspecting equipment, understanding fall arrest mechanics, and emergency rescue procedures.
4. Inspection and Maintenance
Fall protection equipment must be regularly inspected and maintained. Faulty or damaged gear can lead to accidents, even if it meets initial compliance standards.
_________________
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failing to meet OSHA’s fall protection standards can result in serious consequences, including hefty fines and increased liability. In 2023, OSHA's maximum penalty for a serious violation was over $15,000, and willful or repeated violations carried penalties exceeding $156,000. Beyond financial repercussions, non-compliance can lead to injuries, fatalities, and a tarnished business reputation.
_________________
How to Ensure Compliance
Here are practical steps businesses can take to meet OSHA fall protection standards:
-
Conduct Regular Safety Audits
Inspect your workplace for potential fall hazards and implement the necessary protection systems.
-
Invest in Quality Fall Protection Equipment
Use ANSI-tested fall protection gear like harnesses, SRLs, and anchor points to ensure worker safety.
-
Provide Comprehensive Training
Equip your workers with the knowledge and skills to work safely at height and respond to emergencies effectively.
-
Work with Experts
Partner with safety professionals to create a customized fall protection plan for your business.
_________________
Understanding and adhering to OSHA's fall protection standards is not just a regulatory requirement—it’s a moral obligation to protect your workforce. By implementing effective fall protection measures and staying informed on compliance updates, businesses can create a safer work environment and prevent life-altering accidents!
Here at KwikSafety, we specialize in providing OSHA-compliant fall protection solutions. From self-retracting lifelines (SRLs) like our 20FT COBRA SRL to harnesses and anchor systems, we offer products that prioritize safety and durability.
Browse our collection of fall protection gear to find the perfect solution for your workplace. Let us help you stay compliant and keep your workers safe at every height!
OSHA & ANSI Compliance
How to Report OSHA Violations
Workplace safety is paramount to the well-being of employees and the success of any organization. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) enforces safety and health rules nationwide—but OSHA relies on individuals like you to report violations. Here’s how to do it.
This guide explains what an OSHA violation is, the most common issues, and a step-by-step process for filing a complaint to help keep every worksite safer.
Read more
_____
Understanding OSHA Violations
Before reporting, it helps to know the categories OSHA uses to classify issues:
1. Serious Violations
There is a substantial probability of death or serious harm, and the employer should have known about the hazard.
2. Other-Than-Serious Violations
May not cause serious physical harm but still pose health and safety risks to employees.
3. Willful Violations
Deliberate or knowing disregard of OSHA requirements by an employer.
4. Repeat Violations
Cited previously for the same or substantially similar condition and the issue was not corrected.
_____
10 Most Common OSHA Violations
Despite clear rules, some hazards appear again and again. Use this list to focus audits and training.

-
Fall Protection (29 CFR 1926.501): Missing guardrails, unsecured scaffolds, unprotected edges.
-
Hazard Communication (29 CFR 1910.1200): Labels/SDS missing or incomplete; weak HazCom programs.
-
Ladders (29 CFR 1926.1053): Improper use, damaged ladders, wrong ladder for the task.
-
Respiratory Protection (29 CFR 1910.134): No program, poor fit testing, bad storage/maintenance.
-
Scaffolding (29 CFR 1926.451): Assembly/inspection/training deficiencies.
-
Lockout/Tagout (29 CFR 1910.147): Hazardous energy not controlled during servicing.
-
Powered Industrial Trucks (29 CFR 1910.178): Inadequate training, unsafe operation, poor maintenance.
-
Fall Protection – Training (29 CFR 1926.503): Workers near fall hazards not properly trained.
-
Eye and Face Protection (29 CFR 1926.102): Missing goggles/face shields where required.
-
Machine Guarding (29 CFR 1910.212): Missing or inadequate guards on moving parts.
OSHA updates enforcement priorities regularly—stay current to remain compliant.
_____
Reporting OSHA Violations
Anyone can report hazards. Follow these steps to file an effective complaint:
Step #1: Document the Violation
Gather evidence: photos, videos, dates, times, locations, and people involved. Detailed notes help investigators.
Step #2: Inform Your Supervisor
For minor issues, alert your supervisor first if safe to do so. Many employers will correct hazards quickly.
Step #3: Contact OSHA
-
Online: Use OSHA’s tool to submit a complaint.
-
Phone: Call 1-800-321-OSHA (1-800-321-6742).
-
In Person: Visit a local office—find one by state.
Step #4: Provide Detailed Information
Describe the hazard, location, employer, affected workers, and any injuries. You may remain anonymous, but contact info can help OSHA follow up.
Step #5: Follow Up
Check status with OSHA. Inspections or investigations may occur, and your input can be valuable.
_____
Why Reporting Matters
Reporting hazards protects coworkers, holds employers accountable, and improves safety across industries. Your action can prevent injuries—and save lives.
↑ Back to top
↑ Back to top
OSHA & ANSI Compliance
OSHA vs ANSI: What’s the Difference?
OSHA and ANSI both shape workplace safety—but in different ways. OSHA is the federal regulator; ANSI coordinates voluntary consensus standards. Knowing how they interact helps you stay safe and compliant.
Read more
_____
What is OSHA?
OSHA is a U.S. federal agency created by the OSH Act of 1970. Its mission is to ensure safe, healthful working conditions by setting and enforcing rules, and by providing training and outreach.
Key Functions of OSHA:
-
Standard Setting: Issues rules covering fall protection, HazCom, electrical safety, and more.
-
Inspections & Compliance: Conducts inspections; non-compliance can lead to citations and fines.
-
Training & Education: Publishes guidance and funds training for employers and workers.
_____
What is ANSI?
ANSI is a private, non-profit coordinator of the U.S. voluntary consensus standards system. ANSI itself doesn’t regulate; it facilitates standards that improve safety, quality, and interoperability.
Key Functions of ANSI:
-
Standard Development: Oversees voluntary standards across sectors (construction, tech, healthcare).
-
Accreditation: Accredits standards developers using open, consensus-based processes.
-
Promoting Innovation: Enables experts to create/update specs that raise safety and quality.
-
Global Influence: Represents the U.S. in international standardization efforts.
_____
Key Differences Between OSHA and ANSI
-
Regulatory Authority: OSHA is governmental and mandatory; ANSI is non-governmental and voluntary.
-
Enforcement: OSHA enforces via inspections/penalties; ANSI relies on industry adoption.
-
Scope: OSHA focuses on workplace safety/health; ANSI spans products, processes, and systems broadly.
-
Compliance: OSHA rules are required; ANSI standards apply when referenced by law, contracts, or company policy.
_____
Bottom Line
OSHA is the enforcer; ANSI is the consensus playbook. Together they drive safer worksites and better products. Use OSHA to meet legal requirements—and ANSI to reach best practice.
↑ Back to top
↑ Back to top
OSHA & ANSI Compliance
OSHA for Construction: Standards & Compliance Essentials
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets and enforces rules to keep workers safe. For construction firms, meeting OSHA requirements is both the law and a smart way to prevent injuries and downtime.
Read more
_____
Key OSHA Standards and Regulations for Construction
OSHA’s construction rules cover many hazards. Core standards include:
_____
Steps to Ensure Compliance
1. Documentation
- Maintain inspection logs, incident reports, and training records.
- Publish a written safety program with clear procedures.
2. Inspections
- Run internal audits to spot and fix hazards early.
- Routinely inspect equipment, scaffolds, and work zones.
3. Training
- Provide ongoing OSHA training relevant to each task.
- Verify PPE competency and strong hazard communication.
_____
Benefits of Compliance vs. Consequences of Violations
Benefits of Compliance
-
Enhanced Safety: Fewer injuries and fatalities.
-
Legal Protection: Reduced risk of penalties.
-
Improved Productivity: Less downtime; higher morale.
-
Reputation: Demonstrates a safety-first culture.
Consequences of Violations
-
Fines and Penalties: Higher for repeat/willful cases.
-
Legal Liability: Exposure to lawsuits.
-
Operational Delays: Work stoppages and missed deadlines.
-
Reputational Damage: Harder to win future work.
_____
Resources & Next Steps
Stay current with OSHA guidance: visit the OSHA website or contact your local OSHA office. Prioritizing safety protects people—and projects.
Ready to outfit your crew? Explore hi-vis apparel, PPE, and fall protection built for construction.
↑ Back to top
↑ Back to top
OSHA & ANSI Compliance
What Is ANSI? (and What “ANSI Compliant” Really Means)
ANSI is a well-known name in safety—but what is it, exactly? Below we explain what ANSI does, how it shows up in fall protection and hi-vis apparel, and how to verify real compliance (not just marketing claims).
Read more
_____
What is ANSI?
ANSI (the American National Standards Institute) coordinates the U.S. voluntary consensus standards system. It’s a federation of end-users, manufacturers, and subject-matter experts who develop performance requirements for products and services. ANSI itself does not police workplaces—that’s OSHA’s role.
_____
Where You’ll See ANSI in Safety
In PPE and fall protection, ANSI standards guide performance and labeling for products like safety harnesses, safety lanyards, SRLs, and hi-vis vests, shirts, and jackets.
_____
“ANSI Approved” vs. Conformity
Important: Individual products are not “approved” by ANSI or OSHA. Products can conform to applicable standards after a proper conformity assessment (testing + documentation). Claims like “ANSI Approved” should be treated with caution.
Buyer beware: If you see “ANSI Approved/Compliant,” ask for the test report or Certificate of Conformity. No docs, no deal.
_____
Testing & Documentation at KwikSafety
KwikSafety products are tested and inspected by accredited third-party labs. We provide Certificates of Conformity and simplified testing reports upon request. Don’t see a report listed? Email sales@kwiksafety.com and we’ll assist.
Our safety products are ANSI tested and are OSHA compliant, ensuring dependable performance when used in a properly designed system.
_____
Popular ANSI-Tested & OSHA-Compliant Gear
Fall Protection
Safety Apparel
Jackets & Rainwear
Hard Hats
Web Slings
↑ Back to top
↑ Back to top
OSHA & ANSI Compliance
The Importance of ANSI Testing for Safety Products
Safety gear only works if it performs under pressure. ANSI testing creates a consistent bar for quality and reliability so workers can trust their PPE on the job—every time.
Read more
_____
Understanding ANSI
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) coordinates voluntary, consensus-based standards for products, services, and systems. These standards are drafted by cross-industry experts to capture best practices and performance needs.
Want a primer? See our blog: What Is ANSI?
_____
The Importance of ANSI Testing
1) Consistency & Quality
Testing to a common benchmark ensures each unit performs as intended—shift after shift.
2) Compliance with Regulations
Agencies like OSHA often reference ANSI standards. Conformant gear supports legal use across industries.
3) Enhanced Safety
Rigorous requirements for impact, durability, and design help products handle real hazards.
4) Liability Reduction
Documented conformity can reduce organizational risk following an incident.
5) Confidence & Trust
Clear labeling and test records build user confidence and brand credibility.
_____
The Reasoning Behind ANSI Testing
1) Research & Development
Standards evolve through expert input so specs reflect current science and field data.
2) Performance Evaluation
Testing validates impact resistance, electrical properties, ergonomics, and more—spotting weaknesses early.
3) Real-World Simulation
Protocols mimic job conditions (e.g., drop tests for helmets) to verify dependable protection.
_____
Bottom Line
Choosing ANSI-tested PPE gives workers reliable, proven protection. Our safety products are ANSI tested and are OSHA compliant, ensuring consistent performance when integrated into properly designed systems.
↑ Back to top
↑ Back to top
OSHA & ANSI Compliance
What is the Difference Between a Safety Positioning Belt with Suspension Straps and a Safety Harness?
A safety belt with suspension straps may seem like an alternative to a safety harness, but it is not safe to use as a substitute. While it may provide some level of support and security, it lacks crucial features that ensure maximum safety for workers at height.
In this blog post, we will talk about the differences between a Safety Belt with Suspension Straps and a Fall Arrest Safety Harness.
We will also list off what our new Safety Belt with Suspension Straps can be used for
Read more
Safety Belt with Suspension Straps vs. Safety Harness
A safety harness is specifically designed to distribute the forces of a fall evenly across the body, minimizing the risk of injury. It consists of a full-body harness that securely straps around the worker, distributing the impact of a fall across the shoulders, chest, hips, and thighs. This design helps to prevent severe injuries, such as internal organ damage and compression of the rib cage.
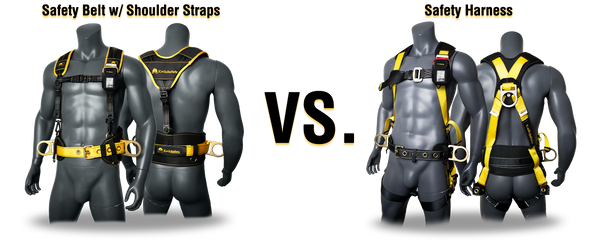
In contrast, a safety belt with suspension straps is a specialized device designed to provide support, stability, and proper positioning for workers. This belt typically consists of a wide strap that wraps around the waist with d-rings on the sides that attach to an anchor point and adjustable shoulder straps that are connected to a central point on the back. The shoulder straps connected to this safety belt provide support and help distribute the belt's weight more evenly. The purpose of this device is to enhance safety by ensuring proper alignment and stability, allowing individuals to maintain an upright posture. While it may provide stability and allow for hands-free work, it lacks the comprehensive protection offered by a safety harness.
Why Can't I Use a Safety Belt with Suspension Straps Instead of a Safety Harness?
Here are a 4 important reasons why a safety belt with suspension straps is NOT a safe alternative to use in replace of a safety harness:
-
Lack of Full-Body Support: A safety belt with suspension straps only provides support around the waist area, leaving the upper and lower body vulnerable in the event of a fall. This limited support can lead to serious injuries, as the forces of impact are concentrated in a smaller area of the body.
-
Potential for Suspension Trauma: In the event of a fall, a worker wearing a safety belt with suspension straps may become suspended in an upright position. Prolonged suspension in this position can cause suspension trauma, also known as harness-induced pathology, which can lead to a loss of consciousness or even death due to the restriction of blood flow to the legs.
-
Inadequate Fall Arrest System: A safety harness is equipped with a shock-absorbing lanyard or self-retracting lifeline that helps absorb the impact of a fall, reducing the forces transmitted to the body. A safety belt with suspension straps lacks this critical component, which significantly increases the risk of injury in the event of a fall.
-
Compliance with Safety Standards: Occupational safety regulations and standards typically mandate the use of safety harnesses for working at height. Employers are responsible for ensuring the safety and well-being of their workers and are expected to adhere to these regulations. Using a safety belt with suspension straps instead of a safety harness may not comply with these standards, potentially exposing workers and employers to legal and financial liabilities.
What is a Safety Positioning Belt with Suspension Shoulder Straps and What is it Used For?
A Safety Positioning Belt with Suspension Straps is a high-performance positioning belt made up of 2 major components:
- Safety Positioning Belt
- Adjustable Shoulder Straps

Shoulder Straps, or Suspension Straps, on a Safety Belt enhance comfort and reduce the risk of musculoskeletal strain.
Here are some ways in which shoulder straps contribute to ergonomic support:
-
Load Distribution: Evenly distributes weight and forces on the body.
-
Posture Support: Promotes proper posture and alignment.
-
Upper Body Stability & Reduction of Fatigue: Provide stability during dynamic movements or in unstable environments and helps to alleviate upper body fatigue
-
Freedom of Movement: Adjustability allows for comfortable movement without compromising safety.
A Safety Positioning Belt, also known as a work positioning belt or tool belt, has various applications in the work industry.
Here are some common uses:
-
Work Positioning: Provides stability and support for elevated tasks, enabling more precise control.
-
Hands-Free Operation: Secures workers to an anchor point while allowing unrestricted hand movement for tasks like window cleaning, painting, & maintenance.
-
Tool and Equipment Storage: Equipped with loops and pouches for convenient tool and equipment carry, improving efficiency.
-
Ergonomic Support: Offers features like lumbar support and padding to reduce lower back strain during extended work periods.
-
PPE Component: Essential personal protective equipment that complements other safety gear for comprehensive worker safety.

**It's crucial to note that the specific use and features of safety positioning belts may vary depending on industry regulations, job requirements, and workplace hazards. Therefore, it is essential to adhere to industry standards and guidelines, as well as receive proper training on their correct usage, inspection, and maintenance.**
__________________________
In conclusion, while a safety belt with suspension straps may provide some support and convenience for ironworkers, it should never be considered a substitute for a safety harness. The comprehensive protection, full-body support, and fall arrest capabilities provided by a safety harness are essential for ensuring the safety and well-being of workers at height.
↑ Back to top
↑ Back to top
OSHA & ANSI Compliance
The True Cost of Not Wearing a Safety Harness: A Financial Breakdown
When it comes to workplace safety, investing in proper fall protection is not just about compliance—it’s about financial responsibility. Some employers and workers may view safety harnesses as an unnecessary expense, but the reality is that the cost of an average harness pales in comparison to the financial burden of OSHA fines, medical expenses, and the cost of replacing an injured employee.
Let’s break it down.
Read more
_____
The Cost of an Average Safety Harness
A standard ANSI-approved full-body safety harness typically ranges from $50 to $300, depending on features such as padding, quick-connect buckles, and durability. Even premium harnesses with enhanced comfort and functionality cost significantly less than the expenses that result from a fall-related incident.
Now, let’s compare that to what happens when a worker is not properly secured.
_____
The Cost of OSHA Fines
OSHA takes fall protection seriously. In 2024, the penalty for a single serious OSHA fall protection violation is $16,131 per incident. If the violation is deemed willful or repeated, the fines can skyrocket to $161,323 per violation.
In many cases, companies face multiple violations at once—meaning fines can quickly reach six figures or more.
_____
Medical Expenses from a Fall Accident
Even if a worker survives a fall, the medical costs can be astronomical. According to the National Safety Council (NSC), the average cost of a fall injury requiring hospitalization is $50,000 or more. Severe falls resulting in permanent disability can lead to millions in medical bills over a lifetime, with expenses covering:
- Emergency medical response
- Surgery and hospitalization
- Rehabilitation and physical therapy
- Long-term disability care
_____
The Hidden Cost: Replacing an Injured Worker
When a worker is injured or unable to return to work, the employer faces productivity losses and replacement costs. This includes:
-
Recruitment & Hiring Costs – The cost to hire a replacement can be 30% to 50% of the worker’s annual salary.
-
Training Costs – Onboarding and training a new worker can range from $1,500 to $5,000.
-
Lost Productivity – It can take months before a new hire reaches full efficiency, resulting in lost revenue.
_____
The Bottom Line: A Harness Pays for Itself
Here’s a quick financial comparison:
| Expense |
Estimated Cost |
| Safety Harness |
$50 – $300 |
| OSHA Fine (per violation) |
$16,131 – $161,323+ |
| Medical Expenses |
$50,000 – $1,000,000+ |
| Replacing a Worker |
$5,000 – $50,000+ |
For less than the price of a single tool or a pair of work boots, a properly worn safety harness can prevent life-altering injuries and save tens (if not hundreds) of thousands of dollars.
_____
Conclusion: Safety is the Smarter Investment
The choice is simple: spend a few hundred dollars on a harness or risk massive fines, medical bills, and workforce disruptions. No job is worth a life, and no company should gamble with the financial consequences of ignoring fall protection.
At KwikSafety, we offer a range of affordable, ANSI-tested safety harnesses designed to keep workers safe and businesses compliant. Investing in safety isn’t just the right thing to do—it’s the smart thing to do.
Need help choosing the right fall protection gear? Browse our selection of high-quality harnesses and fall protection kits today!
Note: The statistics and figures provided are based on available data as of March 2025 and may vary depending on specific circumstances and updates in regulations.
↑ Back to top
↑ Back to top
OSHA & ANSI Compliance
The Evolution of Safety Harnesses
When it comes to workplace safety, few innovations have been as transformative as the safety harness. From rudimentary leather straps to today’s advanced fall protection systems, the history of safety harnesses is one of continuous improvement.
In this post, we’ll explore the evolution of safety harnesses, highlight key advancements, and discuss how modern tech—like self-retracting lifelines (SRLs)—is shaping the future of fall protection.
Read more
_____
The Humble Beginnings: Early Safety Harnesses
The first safety harnesses were simple leather belts and straps used in construction and shipbuilding. They offered limited support and often failed to distribute fall forces, providing minimal comfort or reliability—but they were an important first step.

_____
The Mid-20th Century: Full-Body Harnesses Arrive
Industrial growth and stricter safety expectations in the 1940s–50s drove the development of full-body harnesses that spread arrest forces across the shoulders, chest, hips, and thighs. These became essential for construction, utilities, and other high-risk trades.
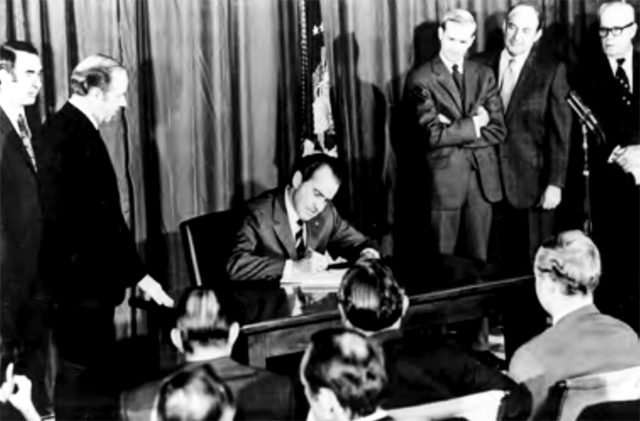
In 1970, the Occupational Safety and Health Act established OSHA and NIOSH, accelerating adoption of reliable fall protection across U.S. worksites.

_____
The Rise of ANSI Standards
ANSI standards set rigorous performance, labeling, and testing criteria for fall protection equipment. By defining strength, durability, and usability benchmarks, ANSI pushed manufacturers to innovate and consistently deliver safer, more reliable harnesses.
_____
Modern Advancements: Comfort to Cutting-Edge
1) Ergonomic Design. Lighter materials, padded contact points, and better adjustability reduce fatigue and improve all-day wearability.
2) Self-Retracting Lifelines (SRLs). Compact devices that manage lifeline slack automatically and stop falls within inches using internal braking—often outperforming traditional lanyards.
3) Enhanced Durability. High-strength polyester webbing and corrosion-resistant hardware withstand UV, chemicals, heat, and cold for longer service life.
_____
The Future of Fall Protection
Expect smarter harnesses with integrated sensors, location awareness, and health monitoring—paired with evolving ANSI standards that continue to raise the bar for protection, usability, and reliability.
_____
From simple leather straps to today’s engineered systems, harness evolution reflects a growing commitment to worker safety. Explore our ANSI-compliant lineup to equip your team with the latest in fall protection innovation.
Shop KwikSafety safety harnesses →
↑ Back to top
↑ Back to top








Leave a comment